Discover 10 fascinating facts about Ancient Rome that you probably didn’t know. Explore its incredible engineering, gladiators, and the iconic Roman Empire. Read now!

The Roman Military: How They Built the Most Powerful Army in History
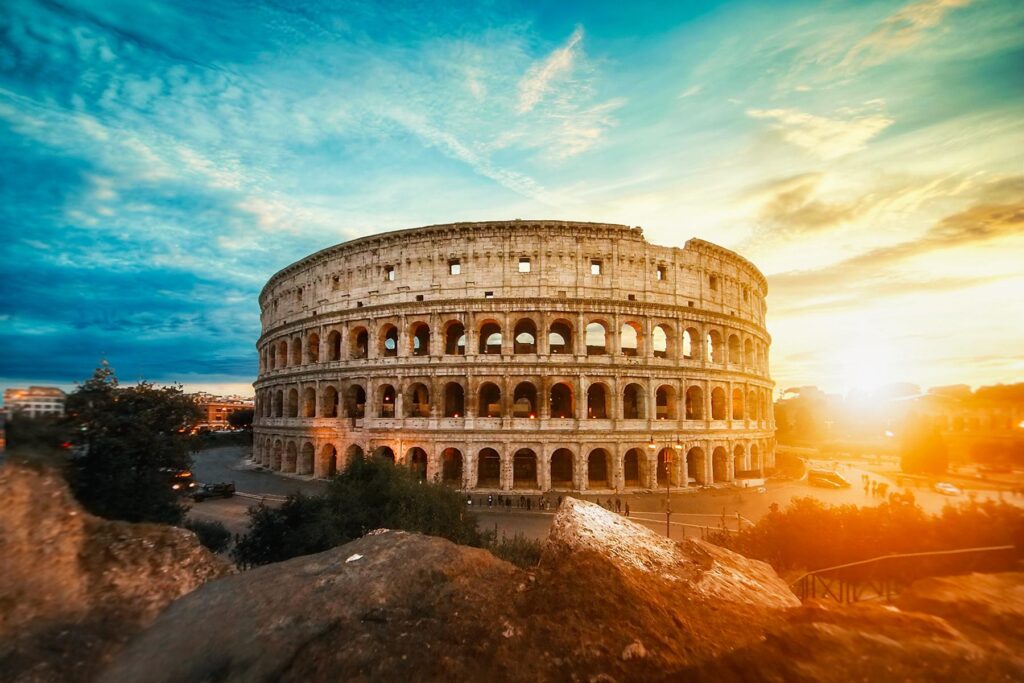
ANCIENT ROME FACT 1. Roman Military Organization Was Highly Efficient: The Roman military was structured into legions, each consisting of approximately 5,000 soldiers. This highly disciplined and well-trained force was crucial to the expansion of the Roman Empire. The Romans also used the “testudo” formation, a tactical maneuver where soldiers formed a protective shield wall, resembling a tortoise, to defend against projectiles such as arrows. This strategic innovation made them nearly unstoppable in battle.
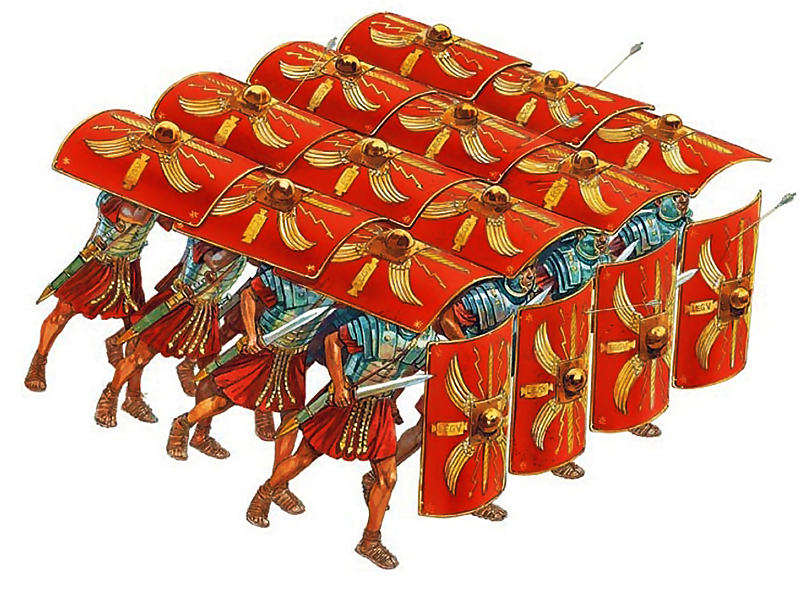

ANCIENT ROME FACT 2. Roman Roads Enabled Unmatched Military Mobility: The Romans built an extensive network of roads throughout the empire, allowing for swift troop movement and effective communication across vast distances. These roads not only helped secure Roman control over its territories but also played a pivotal role in trade and logistics. The famous saying “All roads lead to Rome” refers to the crucial road system that facilitated military dominance and connectivity within the empire.

Gladiators of Rome: The Warriors Who Fought for Glory and Survival
FACT 3. Gladiators Were Highly Trained Fighters: Contrary to the popular belief that gladiators were simply slaves, many were actually trained professionals who volunteered for the arena. These fighters, known as muneri, trained in special schools called ludi to perfect their combat skills. Gladiators followed a strict regimen, learning how to fight with various weapons like swords, tridents, and nets. Their skill level was so advanced that some even became celebrities of their time, with fans and sponsors.

ANCIENT ROME FACT 4. Gladiator Fights Were a Form of Public Entertainment: Gladiator battles were not just brutal spectacles but also served as a way for Roman emperors and politicians to gain favor with the public. These events, called munera, were often held during festivals or political events and could attract thousands of spectators. The Colosseum, Rome’s most iconic arena, could hold up to 50,000 people, making it one of the largest venues for public entertainment in the ancient world. Gladiators were often seen as symbols of strength and valor, celebrated in art and literature.
Rome’s Greatest Arena for Gladiator Battles
FACT 5. The Colosseum Was the Largest Amphitheater of the Roman Empire: The Colosseum, also known as the Flavian Amphitheater, is the largest ancient amphitheater ever built, with a capacity of over 50,000 spectators. It was an architectural marvel, showcasing Roman engineering skills. Its elliptical design and advanced materials allowed the Colosseum to host a variety of public events, including gladiator fights, animal hunts, and mock naval battles. This iconic structure is still considered one of the greatest feats of Roman engineering.
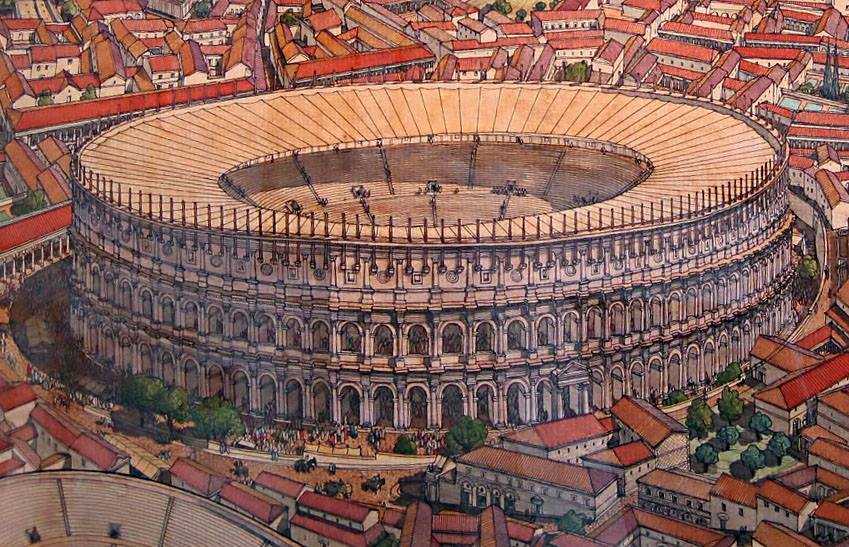
FACT 6. The Colosseum Was Also Used for Mock Naval Battles: One of the most extraordinary features of the Colosseum was its ability to be flooded for mock naval battles, known as naumachiae. These elaborate spectacles simulated naval warfare, with real ships and combatants participating in the staged battles. The arena’s design included a complex system of underground tunnels and chambers that could be flooded with water to create the illusion of a sea battle, providing an unforgettable experience for the audience.
Roman Religion and Gods: Beliefs That Shaped an Empire
ANCIENT ROME FACT 7. Roman Gods Were Incorporated Into Every Aspect of Life: The Romans believed that their gods and goddesses played a central role in both public and private life. From daily rituals to grand festivals, deities like Jupiter, Juno, and Mars were invoked to ensure the well-being of the state and individuals. Roman religion was deeply integrated into the social, political, and military spheres, with temples and altars dedicated to gods found throughout the Empire. This devotion to the gods helped maintain social order and unity across vast territories.
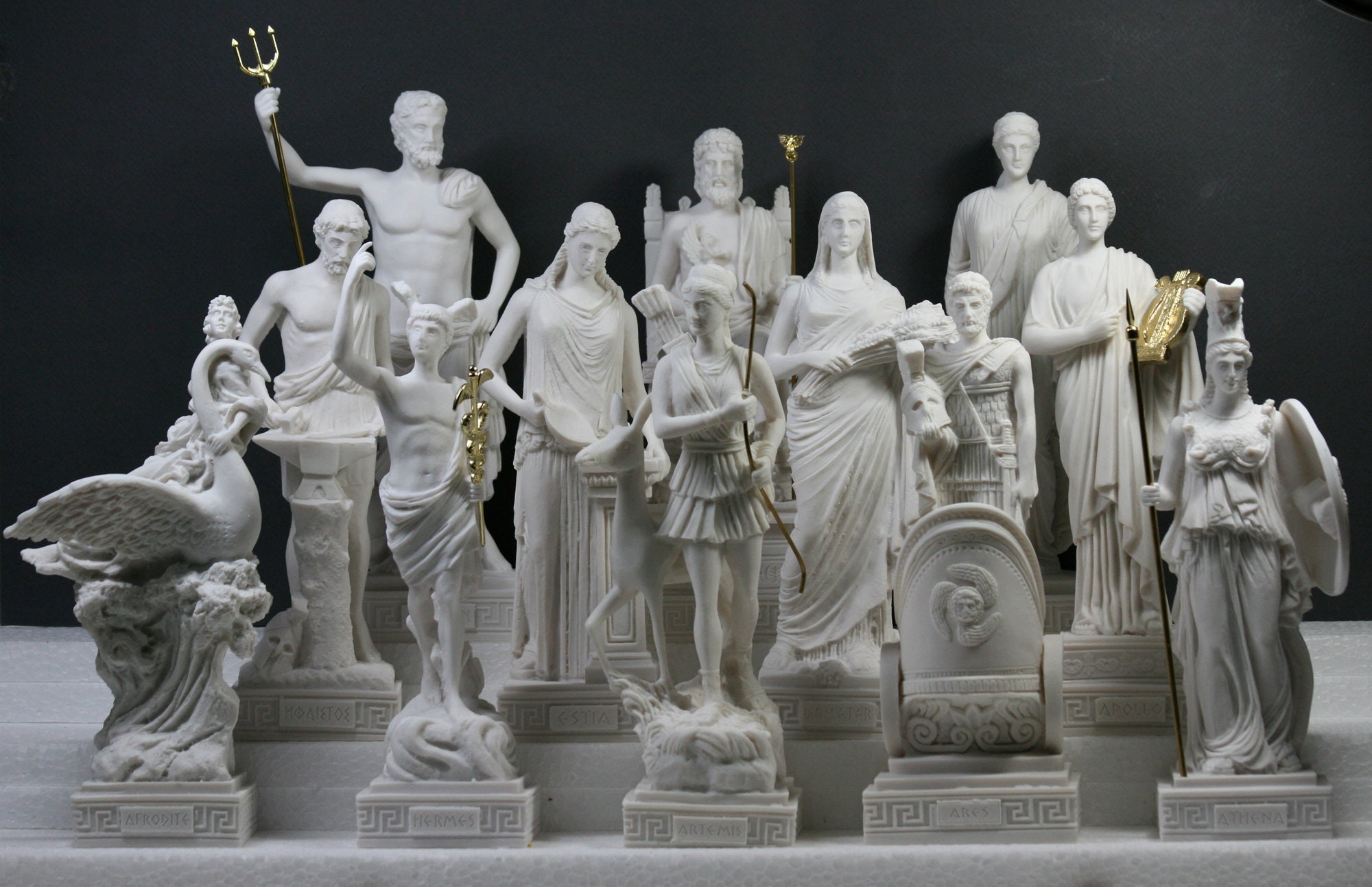

FACT 8. The Roman Pantheon Had a Diverse Range of Gods and Goddesses: The Roman pantheon was vast and included a variety of gods and goddesses that represented various aspects of life, from love and war to fertility and the harvest. One of the most important deities was Jupiter, the king of the gods, who symbolized authority and governance. Other notable gods included Venus, the goddess of love, Apollo, the god of the sun and healing, and Neptune, the god of the sea. Roman religion was also syncretic, meaning they adopted and adapted deities from other cultures, such as the Greek gods, integrating them into Roman beliefs.
Famous Roman Emperors Who Shaped the Empire
FACT 9. Julius Caesar is one of the most famous figures in Roman history. Known for his military genius and political ambition, he played a pivotal role in the transformation of the Roman Republic into the Roman Empire. Caesar’s conquest of Gaul extended Rome’s territory to the Atlantic coast, significantly expanding its influence. His actions, however, led to his assassination in 44 BCE by a group of senators who feared his rising power. Despite his death, Caesar’s reforms and his adoption as the heir by his nephew, Augustus, would lay the foundation for the Roman Empire’s rise.

FACT 10. Augustus, originally known as Octavian, is credited with founding the Roman Empire after the assassination of Julius Caesar. After a series of civil wars, Augustus became the undisputed ruler of Rome and was granted the title “Imperator” by the Senate, effectively making him the first Roman emperor. Under Augustus, Rome experienced a period of peace and prosperity known as the Pax Romana, which lasted for over two centuries. Augustus also undertook significant reforms in Rome’s administration, military, and infrastructure, solidifying his legacy as one of the greatest emperors in history.